23. Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC)
23.1 Confirm the performance of the instrument and the test procedure by analyzing a QC sample.
23.1.1 When QA/QC protocols are already established in the testing facility, these may be used when they confirm the reliability of test result.
23.1.2 When there is no QA/QC protocol established in the testing facility, Appendix X1 may be used as the QA/QC system.
23.2 Users of this test method are advised that in contractual agreements, one or more of the contracting parties can and may make Appendix X1 mandatory practice.
24. Precision and Bias
24.1 Precision - The precision of these test methods as determined by the statistical examination of the interlaboratory test results is as follows:
24.1.1 Repeatability - The difference between successive results obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test materials would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty.
24.1.1.1 Test Method A - Values can be obtained for organically-bound chlorine for any given concentration above 1 µg/g Cl (in the original crude oil specimen) as follows:
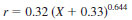
where:
X = µg/g chloride.
24.1.1.2 Test Method B - Values can be obtained for organically-bound chlorine for any given concentration above 1 µg/g Cl (in the original crude oil specimen) as follows:
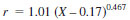
where:
X = µg/g chloride.
24.1.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical material would, in the long run, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty.
24.1.2.1 Test Method A - Values can be obtained for organically-bound chlorine for any given concentration above 1 µg/g Cl (in the original crude oil specimen) as follows:
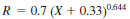
where:
X = µg/g chloride.
24.1.2.2 Test Method B - Values can be obtained for organically-bound chlorine for any given concentration above 1 µg/g Cl (in the original crude oil specimen) as follows:
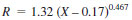
where:
X = µg/g chloride.
24.2 Bias - The bias for either Test Method A or B has been demonstrated by performing analyses using known spiked concentrations of various organic chloride compounds in a variety of crude oils to be lower than the true value. This is because not all of the volatile components will distill from a complex crude oil under the conditions of this test method. The extent of this bias is shown in Fig. 1, where various recoveries are shown plotted against the known concentration of pure organic-chloride compound spikes.
25. Keywords
25.1 coulometry; crude oil; organic chloride; organochlorine; sodium biphenyl

