ASTM D4815 Standard Test Method for Determination of MTBE, ETBE, TAME, DIPE, tertiary-Amyl Alcohol and C1 to C4 Alcohols in Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
13. Procedure
13.1 Preparation of Sample - Transfer 0.5 mL of internal standard (Ws) by a volumetric pipette into a tared and capped 10-mL volumetric flask. Record weight to nearest 0.1 mg. Record the net mass of the internal standard added. Retare the capped flask. Fill the 10-mL volumetric flask to volume with sample, cap, and record the net mass (Wg) to the nearest 0.1 mg of the sample added. Mix thoroughly and inject into the gas chromatograph. If using an automatic sampler, then transfer an aliquot of the solution into a glass gas chromatographic (GC) vial. Seal the GC vial with a TFE-fluorocarbon-lined septum. If the sample is not immediately analyzed, store below 5°C (40°F).
13.2 Chromatographic Analysis - Introduce a representative aliquot of the sample, containing internal standard, into the gas chromatograph, using the same technique and sample size as used for the calibration analysis. An injection volume of 1.0 to 3.0 µL with a 15:1 split ratio has been used successfully. Start recording and integrating devices in synchronization with sample introduction. Obtain a chromatogram or integrated peak report, or both, which displays the retention times and integrated area of each detected component.
13.3 Interpretation of Chromatogram - Compare the retention times of sample components to those of the calibration analysis to determine the identities of oxygenates present.
14. Calculations and Reporting
14.1 Mass Concentration of Oxygenates - After identifying the various oxygenates, measure the area of each oxygenate peak and that of the internal standard. From the least-squares fit calibrations, as depicted in the MTBE example in Fig. 3, calculate the mass of each oxygenate (Wi) in the gasoline samples, using the response ratio (rspi) of the areas of the oxygenate to that of the internal standard as follows:
rspi = (mi)(amti) + bi
where:
mi = slope of the linear fit,
bi = y-intercept, and
amti = amount ratio as defined by Eq 3.
or
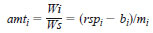
or
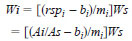
To obtain mass % (wi) results for each oxygenate:
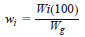
where:
Wg = weight of gasoline sample.
14.2 Report the mass % of each oxygenate to the nearest 0.01 mass %.
14.3 Volumetric Concentration of Oxygenates - If the volumetric concentration of each oxygenate is desired, calculate the volumetric concentration in accordance with Eq 20:
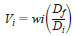
where:
wi = mass % of each oxygenate, as determined using Eq 19,
Vi = volume % of each oxygenate to be determined,
Di = relative density at 15.56°C (60°F) of the individual oxygenate, as found in Table 1, and
Df = relative density of the fuel under study, as determined by Test Method D1298 or D4052.
14.4 Report the volume % of each oxygenate to the nearest 0.01 volume %.
14.5 Mass % Oxygen - To determine the oxygen content of the fuel, convert and sum the oxygen contents of all oxygenated components determined above in accordance with the following equation:
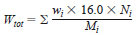
or
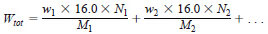
where:
wi = mass % of each oxygenate, as determined using Eq 13,
Wtot = total mass % oxygen in the fuel,
Mi = molecular mass of the oxygenate, as given in Table 1,
16.0 = atomic mass of oxygen, and
Ni = number of oxygen atoms in the oxygenate molecule.
14.6 Report the total mass % of oxygen in the fuel to the nearest 0.01 mass %.

