ASTM D4768 Standard Test Method for Analysis of 2,6-Ditertiary-Butyl Para-Cresol and 2,6-Ditertiary-Butyl Phenol in Insulating Liquids by Gas Chromatography
7. Calibration and Standardization
7.1 Cleanup Column Preparation - Prepare cleanup columns by inserting a small glass wool plug into the wide end of a Pasteur pipet and tamping down to the narrow end. Fill column to a height of approximately 35 mm (1.5 in.) with alumina and place a second glass wool plug on top of adsorbent. Activate column by placing in 325°C oven for a minimum of 12 h. Cool in a desiccator prior to use. After column has cooled, purge column with approximately 2 mL hexane or heptane. Do not allow column to dry out prior to use.
7.2 Standard Solution Preparation - Standard solutions are prepared containing both DBP and DBPC from inhibitor-free mineral oil. Prepare oil solutions of 0, 0.040, 0.080, 0.15, 0.30, and 0.40 % (w/w) of both DBP and DBPC. Determine the relative density (specific gravity) of the oil used in standard solution preparation (DI) to 0.001.
7.3 Column Extraction Efficiency - Verify by the following procedure that the extraction efficiency of the prepared columns is acceptable.
7.3.1 Prepare a check standard containing 0.30 % (w/w) DBP and 0.30 % (w/w) DBPC in methanol. Dilute 0.25 mL of check standard to 5.0 mL with methanol.
7.3.2 Prepare a working standard in accordance with 7.4, using the 0.30 % (w/w) oil standard and the cleanup column whose efficiency is to be determined. Inject a volume of this working standard into the gas chromatograph.
7.3.3 Inject a volume (equal to that used in 7.3.2) of the diluted check standard into the chromatograph using the same chromatographic conditions used to analyze the working standards.
7.3.4 Calculate the extraction efficiency for both DBP and DBPC as follows:
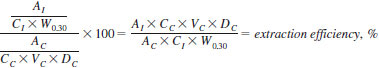
where:
AI = area (or height) of 0.30 % working standard,
AC = area (or height) of 0.30 % check standard,
CI = known concentration of working standard,
CC = known concentration of check standard,
DC = relative density (specific gravity) of methanol used in check standard preparation, and
W0.30 = weight of 0.30 % working standard as recorded in 7.4.1.
VC = volume of check standard diluted to 5 mL in 7.3.1 (=0.25 mL)
7.3.5 The minimum acceptable extraction efficiency is 70 % for DBPC and 60 % for DBP. If the prepared columns do not achieve this level of efficiency, make and test new cleanup columns until acceptable extraction efficiency is achieved. If unable to obtain this, purchase a new lot of acid powder alumina or verify that extraction columns are being activated properly as in 7.1.
7.4 Working Standard Preparation:
7.4.1 Accurately weigh a cleanup column to 0.001 g. Pipet 0.25 mL of the 0 % standard solution onto the top of the cleanup column. Weigh the cleanup column to 0.001 g. Record the difference as W0 %. Repeat for the remaining standard solutions utilizing different cleanup columns and recording weights as W0.040 % , W0.080 %, W0.15 %, W0.30 % and W0.40 %, respectively.
7.4.2 To remove nonpolar interferences, wash the standard solutions with approximately 5 mL of hexane or heptane, collecting the eluate in a waste container. Remove as much of the solvent as possible by using pipet bulb pressure, but do not allow the column to dry out.
7.4.3 Elute the inhibitors from the column with three washes consisting of 1 mL of methanol each, collecting the eluate in a clean 5 mL volumetric flask. Dilute to 5 mL with methanol and mix well. These are the working standards.
7.5 Working Standard Chromatography - Inject a volume of the working standard solution into the equilibrated chromatograph as described in Section 8. Recommended injection volumes are 2 to 10 µL, depending on individual detector response. Measure the response, Ax, (peak height or area in integrator counts) for each peak (excluding the solvent front).
7.5.1 Perform separate linear regression analyses of the responses resulting from both DBPC and DBP working standards by plotting Si versus area, Ax (or height) where:

where:
Si = weight normalized, %.
7.5.1.1 If the correlation coefficient for the regression analyses (7.5.1) is less than 0.995, prepare new working standards (7.4), repeat the chromatographic measurements (7.5) and perform the data analysis (7.5.1) on the new results alone. If the situation is not improved, repeat the procedure using working standards made from newly prepared standard solutions (7.2).
8. Chromatograph Operating Conditions
8.1 General - The characteristics of individual chromatographs and columns differ. Choose particular operating conditions to give a complete separation and good quantification of the peaks obtained. Temperatures and flow rates with which satisfactory separations have been obtained are listed in 8.2 through 8.5.
8.2 Packed or Capillary Column Temperature - A column oven temperature held isothermally at 150°C for 5 min followed by temperature ramping at 20°C/min to 250°C and a hold period at that temperature for 2 min gives satisfactory results. Although the inhibitors are resolved by the isothermal portion of the run, higher temperatures are required to purge the column of interfering substances for successive runs.
8.3 Detector Temperature - A detector temperature of 300°C has been found to be satisfactory.
8.4 Injector Port Temperature - An injector port temperature of 275°C has been found to be satisfactory.
8.5 Carrier Gas - A carrier gas of high purity helium at a flow of 20 to 40 mL/min gives satisfactory results for packed columns.

