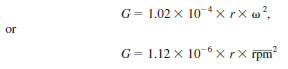ASTM D4425 standard test method for oil separation from lubricating grease by centrifuging (Koppers Method)
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes a procedure for determining the tendency of lubricating grease to separate oil when subjected to high centrifugal forces.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating Grease
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 lubricating grease, n-a semi-fluid to solid product of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
3.1.1.1 Discussion - The dispersion of the thickener forms a two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by surface tension and other physical forces. Other ingredients are commonly included to impart special properties.
3.1.2 thickener, n-in lubricating grease, a substance composed of finely-divided particles dispersed in a liquid to form the products's structure.
3.1.2.1 Discussion - Thickeners can be fibers (such as various metallic soaps) or plates or spheres (such as certain non-soap thickeners), which are insoluble or, at most, only very slightly soluble in the liquid lubricant. The general requirements are that the solid particles be extremely small, uniformly dispersed, and capable of forming a relatively stable, gel-like structure with the liquid lubricant.
3.2 Symbols:
a = distance from top of grease surface to tube mouth (mm).
b = height of liquid column in an inverted test tube (mm).
d = test tube inside diameter (mm).
H = accumulated test time at a given reading (h).
K36 = resistance to centrifugal separation (V/H).
r = measured at the maximum radius of rotation (mm).
rpm = rotational speed (r/min).
V = volume of separated oil, as a percentage of the original grease volume (%).
Vg = grease volume in a test tube (cm3).
Vo = volume of separated oil (cm3).
Vt = test tube total volume (cm3).Vt
A = angle of rotor, between the test tube axis and axis of rotation (degrees).
w = rotational speed (rad/s).
G = relative centrifugal acceleration.
The relative effect of centrifugal forces, when related to the gravitational standard acceleration (9.81 m/s2), is noted with the symbol G. It can be calculated as follows: