11. Calculations
11.1 Calculate the water content of the sample as follows:
water, mass % = CF/W (10)
where:
C = Karl Fischer reagent required to titrate the sample, mL,
F = water equivalence of Karl Fischer reagent, mg/mL,
W = sample used, g, and
10 = factor for converting to percent.
12. Precision and Bias
12.1 The precision of this test method as determined by the statistical examination of interlaboratory test results is as follows:
12.1.1 Repeatability - The difference between successive results obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test material would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty. (See Table 2.)
12.1.1.1 Standard Karl Fischer Reagents:
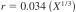
12.1.1.2 Pyridine-Free Karl Fischer Reagents:
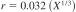
where:
X = sample mean from 0.0 to 2 %.
12.1.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test material would, in the long run, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty.
12.1.2.1 Standard Karl Fischer Reagents:
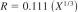
12.1.2.2 Pyridine-Free Karl Fischer Reagents:
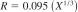
where:
X = sample mean from 0.00 to 2 %.
12.2 Bias:
12.2.1 Compared to the results of Test Method D4006 (API MPMS Chapter 10.2), no significant bias was found.
12.2.2 The interference from mercaptan sulfur follows the theoretical stoichiometry of 1 to 0.28, that is 1000 µg/g (ppm) of mercaptan sulfur can generate a response equivalent to 280 µg/g (ppm) (0.03 mass %) water by this test method. The validity of correcting measured water contents for known mercaptan/sulfide sulfur levels has not been evaluated.
13. Keywords
13.1 crude oils; Karl Fischer reagent; titration; water



