S(numerical specification maximum) - indicates the maximum sulfur content, in weight ppm (µg/g), allowed by this specification.
SA, n - abbreviation for severity adjustment.
SAE - abbreviation for Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc.
salt water, n - the aerobic, aqueous compartment, characteristically with a salinity equal to or greater than five parts per thousand.
sample, n - a part taken as representative of a whole material.
sample division - the process whereby a sample is reduced in mass without change in particle size.
sample preparation - the process that may include drying, crushing, division, and mixing of a gross sample for the purpose of obtaining an unbiased analysis sample.
sample reduction - the process whereby a sample is reduced in particle size by crushing or grinding without significant change in chemical properties.
sample system lag time - the time required to transport a representative sample from the process tap to the analyzer.
saponification, n - the interaction of fats, fatty acids, or esters generally with an alkali to form the metallic salt, which is commonly called soap.
DISCUSSION - Soap thickeners are most often made by in situ saponification in the lubricating grease base oil. However, the use of pre-formed soaps is also common; dispersion is effected by mechanical means and usually with heat.
saponification number, n - in petroleum technology, the number of milligrams of potassium hydroxide that is consumed by 1 g of oil under the conditions of the test.
saponification number, n - the number of milligrams of potassium hydroxide consumed by 1 g of a sample under the conditions of the test.
DISCUSSION - The value of the saponification number in these test methods can be affected by the presence of other alkali-reactive species, as described in Note 1.
saponify, v - to hydrolyze a fat with alkali to form an alcohol and the salt of a fatty acid.
saturates, n - hydrocarbon components that are not retained strongly by the specified polar columns when heptane is used as the mobile phase.
DISCUSSION - Generally, these consist of paraffins and cycloparaffins.
Saybolt color, n - an empirical definition of the color of a clear petroleum liquid.
Saybolt color, n - the name of an empirical scale for expressing of the color of a clear petroleum liquid based on a scale of 16 (darkest) to +30 (lightest) and determined by Test Method D156.
scoring, n - in tribology, a severe form of wear characterized by the formation of extensive grooves and scratches in the direction of sliding.
scoring, n - the formation of severe scratches in the direction of sliding.
DISCUSSION - Scoring may be due to local solid phase welding or to abrasion. The term scuffing is sometimes used as a synonym for scoring.
scoring, n - on ring and pinion gears, the rapid removal of metal from the tooth surfaces caused by the tearing out of small contacting particles that have welded together as a result of metal-to-metal contact. The scored surface is characterized by a matte or dull finish.
scrape sample, n - a portion of residue removed from a surface by forceful strokes of an instrument such as a spatula.
scratches, n - the result of mechanical removal or displacement, or both, of material from a surface by the action of abrasive particles or protuberances sliding across the surfaces.
scratching, n - the formation of fine lines in the direction of sliding that may be due to asperites on the harder slider or to hard particles between the surfaces or embedded in one of them.
DISCUSSION - Scratching is considered less damaging than scoring or scuffing.
scuff, scuffing, n - in lubrication, damage caused by instantaneous localized welding between surfaces in relative motion which does not result in immobilization of the parts.
scuffing, n - in lubrication, damage caused by instantaneous localized welding between surfaces in relative motion that does not result in immobilization of the parts.
scuffing, n - in lubrication, surface damage resulting from localized welding at the interface of rubbing surfaces with subsequent fracture in the proximity of the weld area.
scuffing, n - localized damage caused by the occurrence of solid phase welding between sliding surfaces, without local surface melting.
DISCUSSION - The term scoring is sometimes used as a synonym for scuffing.
scum, n - layer thicker than film (up to 1 mL in volume) or that adheres to the wall of the glass test tube, or both.
seizure, n - in lubrication, welding between surfaces in relative motion that results in immobilization of the parts.
seizure or welding, n - localized fusion of rubbing metal, usually indicated by streaks of transferred metal, increased friction and wear, or unusual noise and vibration.
semi-solid, n - material that is seemingly a solid, except that it deforms slowly under a gravitational force, and it can be made to flow by this force or a greater force.
DISCUSSION - In the petroleum industry, grease, petrolatum, asphalt, and other very viscous materials are recognized as semi-solids. (Synonyms - semi-liquid and semi-fluid.)
shear, adj - a relative movement of molecules or molecular aggregates that occurs in flowing liquids. A shear flow is one in which the spatial velocity gradient is perpendicular to the direction of flow.
DISCUSSION - Not all flow geometries meet this definition.
shear, v - to subject a liquid to shear flow.
DISCUSSION - Shearing an oil can sometimes cause scission of certain molecular species, resulting in a decrease in viscosity. Not all oils exhibit this response. Common ways of shearing oils to elicit this effect include injection through a small orifice and flow through gears or bearings. Irradiation with sonic energy can also decrease the viscosity of some oils.
shear degradation, n - the decrease in molecular weight of a polymeric thickener (VI improver) as a result of exposure to high shear stress.
shear rate, n - in fluid flow, the velocity gradient across the fluid.
shear rate, n - the velocity gradient in fluid flow.
shear rate, n - the rate at which a series of adjacent layers of grease move with respect to each other; proportional to the linear velocity of flow divided by the capillary radius, and is thus expressed as reciprocal seconds.
shear rate, n - the velocity gradient in fluid flow. The SI unit for shear rate is the reciprocal second (s(-1)).
shear rate - the velocity gradient in fluid flow. For a Newtonian fluid in a concentric cylinder rotary viscometer in which the shear stress is measured at the inner cylinder surface (such as this apparatus, described in 6.1), and ignoring any end effects, the shear rate is given as follows:

DISCUSSION - For the specific apparatus being described in 6.1.1,
Gr = 63/t
shear stability, n - the resistance of a polymer-thickened fluid to shear degradation.
shear stress, n - the motivating force per unit area for fluid flow.
shear stress, n - the motivating force per area for fluid flow. The area is the area of shear. In the SI, the unit for shear stress is the Pascal (Pa).
shear stress - the motivating force per unit area for fluid flow. The area is the area under shear.
shear stress - the motivating force per unit area for fluid flow. For the rotary viscometer being described, the rotor surface is the area under shear or the shear area.
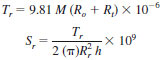
where:
Tr = torque applied to rotor, N•m,
M = applied mass, g,
Ro = radius of the shaft, mm,
Rt = radius of the string, mm,
Sr = shear stress at the rotor surface, Pa, and
h = height of the rotor, mm.
DISCUSSION - For the dimensions given in 6.1.1,
Tr = 31.7 M x 10(-6)
Sr = 3.5 M
shelf life, n - the period of time, under specified storage conditions, for which the reference material (RM) will possess the same properties or true values, within established acceptance limits.
shock treatment, n - the addition of an antimicrobial agent sufficient to cause rapid and substantial (several orders of magnitude) reductions in number of living microbes in a fluid or system receiving that concentration.
SI - abbreviation for Le Système International d'Unités (SI), The International System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System.
SIG, adj - stay-in-grade
DISCUSSION - Capability of multiviscosity-graded oil to stay in grade under test conditions.
single base, adj - in lubricating grease, relating to a thickener comprised of soaps of only one metal.
site precision, n - 2.77 times the standard deviation of results obtained under site precision conditions.
site precision (R'), n - the value below which the absolute difference between two individual test results obtained under site precision conditions may be expected to occur with a probability of approximately 0.95 (95 %). It is defined as 2.77 times the standard deviation of results obtained under site precision conditions.
site precision conditions, n - conditions under which test results are obtained by one or more operators in a single site location practicing the same test method on a single measurement system using test specimens taken at random from the same sample of material over an extended period of time spanning at least a 15 day interval.
DISCUSSION - A measurement system may comprise multiple instruments being used for the same test method.
skinnogen, n - (Synonym - biofilm.)
DISCUSSION - Generally applied to a biofilm formed at the fuel-water interface.
slice time, n - the retention time at the end of a given area slice.
slice width, n - the fixed duration (1 s, or less) of the retention time intervals into which the chromatogram is divided. It is determined from the reciprocal of the frequency used in the acquisition of data.
sludge, n - in internal combustion engines, a deposit, principally composed of insoluble resins and oxidation products from fuel combustion and the lubricant, that does not drain from engine parts but can be removed by wiping with a cloth.
sludge, n - a precipitate or sediment from oxidized mineral oil and water.
sludge, n - in manual transmissions and final drive axles, a deposit principally composed of the lubricating oil and oxidation products that do not drain from parts but can be removed by wiping with a cloth.
smoke point, n - the maximum height of a smokeless flame of fuel burned in a wick-fed lamp.
soap, n - in lubricating grease, a product formed in the saponification (neutralization) of fats, fatty acids, or esters by inorganic bases.
soft carbon, n - see graphitizable carbon.
solid, adj - describing a state of matter characterized by imperceptible flow under moderate stress, a definite capacity for resisting forces that tend to deform it, and, under ordinary conditions, retaining a definite size and shape.
DISCUSSION - A quantity of solid particles, powders, or pellets, for example, fluidized catalyst beds, can also flow like a liquid in the presence of an applied force. The state of the individual particles, nevertheless, remains as a solid.
solid, n - substance (matter) in a solid state (see solid, adj).
solidification point, n - of petroleum wax, that temperature in the cooling curve of the wax where the slope of the curve first changes significantly as the wax sample changes from a liquid to a solid state.
solidification point of petroleum wax, n - that temperature in the cooling curve of the wax where the slope of the curve first changes significantly as the wax sample changes from a liquid to a solid state.
solubility parameter, n - of liquids, the square root of the heat of vaporization minus work of vaporization (cohesive energy density), per unit volume of liquid, at 298 K.
soluble oil, n - an oil-rich concentrate that will mix with water to form an emulsion imparting such properties as lubrication, cooling, and corrosion inhibition.
sonication, n - the act of subjecting a material to the shearing forces of high-frequency sound waves.
DISCUSSION - Sonication of a two phase liquid system may result in the dispersal of one phase as fine droplets in the other phase.
soot, n - in internal combustion engines, sub-micron size particles, primarily carbon, created in the combustion chamber as products of incomplete combustion.
sour, v - to increase the concentration of hydrogen sulfide.
Soxhlet apparatus, n - a device, usually of glass, used to extract soluble material from a mixture of soluble and insoluble (generally solid) materials, by passing a volatile solvent through the sample and recirculating the solvent by refluxing.
spalling, n - on ring and pinion gears, the breaking out of flakes of irregular area of the tooth surface, a condition more extensive than pitting.
spark plug fouling, n - deposition of essentially non-conducting material onto the electrodes of a spark plug that may, but will not necessarily, prevent the plug from operating.
spark plug whiskering, or spark plug bridging, n - a deposit of conductive material on the spark plug electrodes that tends to form a bridge between them, thus shorting out the plug.
spatulate, n - to mix or blend by spreading and folding with a flat thin, usually metal, tool.
special-duty propane - a high-quality product composed chiefly of propane, which exhibits superior antiknock characteristics when used as an internal combustion engine fuel.
specimen, n - a piece or portion of a sample used to make a test.
specular gloss, n - in waxed paper and paperboard technology, the degree to which a surface simulates a mirror in its capacity to reflect incident light.
specular gloss, n - the degree to which a surface simulates a mirror in its capacity to reflect incident light.
specific gravity, n - deprecated term, the ratio of the density of a substance to that of a reference substance such as water (for solids and liquids) or hydrogen (for gases) under specified conditions (see relative density).
split/splitless injector, n - a heated capillary inlet or sample introduction system that allows controlled splitting of the injected sample into two unequal portions, the smaller of which goes to the capillary column, and the greater to a vent.
DISCUSSION - When the vent is closed, the entire sample enters the capillary column and the inlet is operated as a splitless injector. When the vent is open, the inlet is operated in the split mode and only a portion of the sample reaches the capillary column. The ratio of the split between the capillary column and the vent is calculated as described in 3.1.7.2.
split ratio, n - in capillary gas chromatography, the ratio of the total flow of carrier gas to the sample inlet versus the flow of the carrier gas to the capillary column, expressed by:
split ratio = (S + C)/C
where:
S = flow rate at the splitter vent, and
C = flow rate at the column outlet.
sponsor, n - of an ASTM test method, an organization that is responsible for ensuring supply of the apparatus used in the test procedure portion of the test method.
DISCUSSION - In some instances, such as a test method for chemical analysis, an ASTM working group can be the sponsor of a test method. In other instances, a company with a self-interest may or may not be the developer of the test procedure used within the test method, but is the sponsor of the test method.
spread, n - in knock measurement, the sensitivity of the detonation meter expressed in knockmeter divisions per octane number.
SRV, n - Schwingung, Reibung, Verschleiss, (German); oscillating, friction, wear, (English translation).
stability reserve, n - in petroleum technology, the property of an oil to maintain asphaltenes in a peptized state and prevent flocculation of the asphaltenes.
DISCUSSION - An oil with a low stability reserve is likely to undergo flocculation of asphaltenes when stressed (for example, extended heated storage) or blended with a range of other oils. Two oils each with a high stability reserve are likely to maintain asphaltenes in a peptized state and not lead to flocculation when blended together.
stability testing, n - tests required to demonstrate the chemical stability of the ampulized reference material (RM) for the purpose of determining the shelf life of the RM.
stable engine conditions, n - for octane rating, cylinder head temperatures change less than 5°C (9°F) during a 1 min period. Any changes or minor adjustments to throttle, mixture, or engine conditions mandate restarting the clock for determining stable conditions.
standard, n - a physical or chemical reference used as a basis for comparison or calibration.
standard deviation, n - the most usual measure of the dispersion of observed values or results expressed as the positive square root of the variance.
standard knock intensity, n - for knock testing, that level of knock established when a primary reference fuel blend of specific octane number is used in the knock testing unit at maximum knock intensity fuel-air ratio, with the cylinder height (dial indicator or digital counter reading) set to the prescribed guide table value. The detonation meter is adjusted to produce a knockmeter reading of 50 for these conditions.
standard knock intensity, n - for supercharge method knock testing, trace or light knock as determined by ear.
DISCUSSION - Light knock intensity is a level definitely above the commonly defined least audible "trace knock"; it is the softest knock that the operator can definitely and repeatedly recognize by ear although it may not be audible on every combustion cycle (intermittent knock). The variations in knock intensity can occasionally include loud knocks and very light knocks. These variations can also change with mixture ratio; the steadiest knock typically occurring in the vicinity of 0.09 fuel-air ratio.
standard test, n - a test on a calibrated test stand, using the prescribed equipment that is assembled according to the requirements in the test method, and conducted according to the specified operating conditions.
DISCUSSION - The specified operating conditions in some test methods include requirements for determining a test's operational validity. These requirements are applied after a test is completed, and can include (1) mid-limit ranges for the average values of primary and secondary parameters that are narrower than the specified control ranges for the individual values, (2) allowable deviations for individual primary and secondary parameters from the specified control ranges, (3) downtime limitations, and (4) special parameter limitations.
standard test, n - a test on a calibrated test stand, using the prescribed equipment according to the requirements in the test method, and conducted according to the specified operating conditions.
DISCUSSION - The specified operating conditions in some test methods include requirements for determining a test's operational validity. These requirements are applied after a test is completed and can include (1) mid-limit ranges for the average values of primary and secondary parameters that are narrower than the specified control ranges for the individual values, (2) allowable deviations for individual primary and secondary parameters for the specified control ranges, (3) downtime limitations, and (4) special parameter limitations.
starting torque, n - the maximum torque measured at the start of rotation.
state of matter, n - condition in which a substance (matter) exists, as a gas, liquid, or solid.
DISCUSSION - Gas, liquid, and solid are the primary states of matter encountered in the petroleum industry. However, greases, petrolatum, and other very viscous materials are often described as semi-solids (semi-liquids or semi-fluids) because they retain their shapes for extended periods, but can be caused to flow when a force is applied, as is a grease gun. The existence of other physical states of matter, such as plasma and supercritical fluid, is also recognized, as is their application in instrumental and other analyses.
static hold-up or wettage, n - the quantity of liquid retained in the column after draining at the end of a distillation.
DISCUSSION - It is characteristic of the packing or the design of the plates, and depends on the composition of the material in the column at the final cut point and on the final temperature.
storage point, n - an indication of the minimum temperature to which an oil should be heated in any part of an oil-handling installation when starting up after a shutdown. It is also an indication of the minimum temperature at which the oil should be stored in a tank fitted with an outflow heater.
storage stability, n - the resistance of fuel to formation of degradation products when stored at ambient temperatures.
straight-run gases, n - hydrocarbon gases that do not contain unsaturates.
stripping, n - the process whereby volatile fractions are removed from a liquid material.
DISCUSSION - In this test method, lighter components such as water and gasoline are removed by the application of heat while passing an inert gas through the liquid.
strong surfactants, n - in petroleum fuels, surface active materials that disarm filter separator elements.
DISCUSSION - Strong surfactants can be refinery process chemicals left in the fuel or contaminants introduced during transportation of the fuel.
stuck lifter, n - in internal combustion engines, a lifter plunger that does not return to its original position by its own force upon removal from the engine.
sulfate reducing bacterial (SRB), pl., n - any bacteria with the capability of reducing sulfate to sulfide.
DISCUSSION - The term SRB applies to representatives from a variety of bacterial taxa that share the common feature of sulfate reduction (SO4~ to S~). SRB are major contributors to MIC.
sulfated ash, n - the residue remaining after the sample has been carbonized, and the residue subsequently treated with sulfuric acid and heated to constant weight.
sum of squares, n - in analysis of variance, a contraction of the expression "sum of the squared deviations from the appropriate average(s)" where the average(s) of interest may be the average(s) of specific subset(s) of data or of the entire set of data.
supercharge performance number, n - a numerical value arbitrarily assigned to the supercharge ratings about 100 ON.
supercharge rating, n - the numerical rating of the knock resistance of a fuel obtained by comparison of its knock-limited power with that of primary reference fuel blends when both are tested in a standard CFR engine operating under the conditions specified in this test method.
supercritical fluid, n - fluid maintained in a thermodynamic state above its critical temperature and critical pressure.
supercritical fluid chromatography, n - class of chromatography that employs supercritical fluids as mobile phases.
supernatant, n - the liquid above settled solids.
supplier, n - any individual or organization responsible for the quality of a product just before it is taken over by the receiver.
surfactants, n - surface active molecular species that exhibit both water soluble and oil soluble properties, and affect the physical behavior at the interface between water and oil phases by forming emulsions or changing the wetting characteristics of solid surfaces exposed to water and oil.
surfactants, n - in petroleum fuels, surface active materials that could disarm (de-activate) filter separator (coalescing) elements so that free water is not removed from the fuel in actual service.
DISCUSSION - Technically, surfactants affect the interfacial tension between water and fuel which affects the tendency of water to coalesce into droplets or not.
surface finish, n - the geometric irregularities in the surface of a solid material. Measurement of surface finish shall not include inherent structural irregularities unless these are the characteristics being measured.
surface tension (γ), n - the specific surface free energy of a liquid gas interface, millinewton per metre (ergs/cm2).
surrogate calibration, n - a multivariate calibration that is developed using a calibration set which consists of mixtures with pre-specified and reproducible compositions that contain substantially fewer chemical components than the samples which will ultimately be analyzed.
surrogate method, n - a standard test method that is based on a surrogate calibration.
suspended solids (of activated sludge or other inoculum samples), n - solids present in activated sludge or inoculum samples that are not removed by settling under specified conditions.
syneresis, n - of lubricating greases, the separation of liquid lubricant from a lubricating grease due to shrinkage or rearrangement of the structure.
DISCUSSION - Syneresis is a form of bleeding caused by physical or chemical changes of the thickness. Separation of free oil or the formation of cracks that occur in lubricating greases during storage in containers is most often due to syneresis.
synthetic, adj - in lubricants, originating from the chemical synthesis of relatively pure organic compounds from one or more of a wide variety of raw materials.
system noise, n - the difference between the maximum and minimum area readings per second for the first 20 area readings in the blank run.
system response time - the sum of the analyzer unit response time and the analyzer sample system lag time



