5. Apparatus
5.1 Buret, 10-mL capacity, 0.05-mL subdivisions.
5.2 Constant-Temperature Bath, equipped to hold several 100-mL volumetric flasks submerged to the mark. Bath must have a large enough reservoir or heat capacity to keep the temperature at 82.2 to 87.8°C (180 to 190°F) during the entire period of sample heating.
NOTE 1 - If the temperature of the hot water bath drops below 82.2°C (180°F), the color development cannot be complete.
5.3 Cooling Bath, equipped to hold several 100-mL volumetric flasks submerged to the mark in ice water.
5.4 Filter Paper, for quantitative analysis, Class G for fine precipitates as defined in Specification E 832.
5.5 Ignition Dish - Coors porcelain evaporating dish, glazed inside and outside, with pourout (Size No. 00A, diameter 75 mm, capacity 70 mL).
5.6 Spectrophotometer, equipped with a tungsten lamp, a red-sensitive phototube capable of operating at 830 nm and with absorption cells that have a 5-cm light path.
5.7 Thermometer, ASTM 34C or 34F, range from 25 to 105°C (77 to 221°F).
5.8 Volumetric Flask, 100-mL with ground-glass stopper.
5.9 Volumetric Flask, 1000-mL with ground-glass stopper.
5.10 Syringe, Luer-Lok, 10-mL equipped with 5-cm, 22-gage needle.
6. Reagents
6.1 Purity of Reagents - Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where such specifications are available. Other grades may be used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of the determination.
6.2 Purity of Water - Unless otherwise indicated, references to water shall be understood to mean reagent water as defined by Types II or III of Specification D1193.
6.3 Ammonium Molybdate Solution - (Warning - Poisonous gas may be liberated in fire. Irritating to skin and eyes. Harmful if swallowed.)(Warning - In addition to other precautions, wear a face shield, rubber gloves, and a rubber apron when adding concentrated sulfuric acid to water.) Using graduated cylinders for measurement, add slowly, with continuous stirring, 225 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4, relative density 1.84) to 500 mL of water contained in a beaker placed in a bath of cold water. Cool to room temperature, and add 20 g of ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate ((NH4)6Mo7O24•4H2O). Stir until solution is complete and transfer to a 1000-mL flask. Dilute to the mark with water.
6.4 Hydrazine Sulfate Solution - Dissolve 1.5 g of hydrazine sulfate (Warning - Cancer suspect agent.) (H2NNH2•H2SO4) in 1 L of water, measured with a graduated cylinder. (Warning - This solution is not stable. Keep it tightly stoppered and in the dark. Prepare a fresh solution after 3 weeks.)
6.5 Molybdate-Hydrazine Reagent - Pipet 25 mL of ammonium molybdate solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask containing approximately 50 mL of water, add by pipet 10 mL of H2NNH2• H2SO4 solution, and dilute to 100 mL with water.
NOTE 2 - This reagent is unstable and is to be used within about 4 h. Prepare it immediately before use. Each determination (including the blank) uses 50 mL.
6.6 Phosphorus, Stock Solution, Standard (1.00 mg P/mL) - Dry approximately 5 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) in an oven at 105 to 110°C (221 to 230°F) for 3 h. Dissolve 4.393 more or less 0.002 g of the reagent in 150 mL, measured with a graduate cylinder, of H2SO4(1 + 10) contained in a 1000-mL volumetric flask. Dilute with water to the mark.
6.7 Phosphorus Solution, Standard (10.0 µg P/mL) - Pipet 10 mL of phosphorus stock standard solution into a 1000-mL volumetric flask and dilute to the mark with water.
6.8 Sulfuric Acid (1 + 10) - (Warning - Concentrated sulfuric acid causes severe burns. Strong oxidizer.) (Warning - In addition to other precautions, wear a face shield, rubber gloves, and a rubber apron when adding concentrated sulfuric acid to water.) Using graduated cylinders for measurement, add slowly, with continuous stirring, 100 mL of H2SO4 (relative density 1.84) to 1 L of water contained in a beaker placed in a bath of cold water.
6.9 Zinc Oxide - (Warning - See 6.8.) (Warning - High-bulk density zinc oxide can cause spattering. Density of approximately 0.5 g/cm3 has been found satisfactory.)
6.10 Quality Control (QC) Samples, preferably are portions of one or more liquid petroleum materials that are stable and representative of the samples of interest. These QC samples can be used to check the validity of the testing process as described in Section 11.
7. Sampling
7.1 Take samples in accordance with the instructions in Practice D4057.
7.2 Use the following table as a guide for selecting sample size:
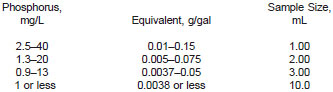
NOTE 3 - When using a 10-mL sample, ignite aliquots of 2 mL of sample in the same 2-g portion of zinc oxide; allow the zinc oxide to cool before adding the next 2-mL aliquot of gasoline (Note 5).

