7. Reference Standards
7.1 Samples of the following hydrocarbons will be required: 2-methylpentane, 2,4-dimethylpentane, n-octane, methylcyclopentane, methylcyclohexane, cis-1,2-dimethylcyclohexane, benzene, toluene, and p-xylene (Warning - see Note 4). Only reagent grade chemicals conforming to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standard hydrocarbon samples, or other hydrocarbons of equal purity should be used.
NOTE 4 - Warning: Extremely flammable liquids. Benzene is a poison, carcinogen, and is harmful or fatal if swallowed.
8. Performance Test
8.1 Calibration for Test Mixture - Calibrate the instrument in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions for the compounds listed in 7.1, using the same manipulative technique as described in 10.2. Express the calibration data in units of peak height per unit of liquid volume (V) at constant sensitivity. Determine ∑41/V, ∑43/V, and ∑77/V for each of the reference standards and calculate a weighted average value for each hydrocarbon group type in accordance with the composition of the test mixture as described in 8.2. Construct an inverse from the averaged coefficients.
NOTE 5 - The volume, V, ordinarily is expressed as microlitres.
NOTE 6 - A desk calculator frequently is used for the calculation of 8.1 and in such cases small inverse terms can be undesirable. If necessary, it is permissible to divide all averaged coefficients by some suitable constant prior to inversion in order to obtain larger values in the inverse.
8.2 Test Mixture - Prepare the synthetic mixture by weight from reference standards to obtain a final composition approximating the following but accurately known within +/- 0.07 %:
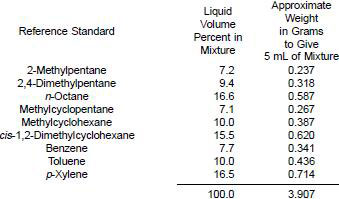
Record the mass spectrum of the test mixture from m/e(+) 32 to 120 using the manipulative technique as described in 10.2. Compute ∑41/V, ∑43/V, and ∑77/V from the spectrum of the test mixture and calculate the composition using these values and the inverse of 8.1. The calculated composition should agree with known concentrations within the following limits:

If the test mixture cannot be analyzed successfully, consideration should be given to interference, stability, sensitivity, resolution, sample handling, or ability of the analyst.
8.3 Background - After pumping out the test mixture specified in 10.2, scan the mass spectrum from m/e(+) 40 to 100. Background peaks at 43 and 91 should be less than 0.1 % of the corresponding peaks in the mixture spectrum. If both tests of performance are met, it may be presumed that the instrument is satisfactory for sample analysis.
9. Sample Preparation
9.1 Depentanize the sample in accordance with Test Method D2001.
9.2 Determine the olefin content of the depentanized sample in accordance with Test Methods D1319 or D875.

