8. Procedure
8.1 Select the solvent to be used and fill the solvent cup as described in 7.2. Weigh into a 25 mL volumetric flask the amount of sample suggested in the following table (Note 2):
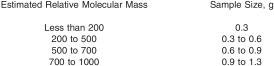
Record the mass to the nearest 0.1 mg and dilute to volume with solvent.
NOTE 5 - If the amount of sample is limited, weigh the sample into a 5 mL or 1 mL volumetric flask, using one-fifth or one twenty-fifth respectively of the amount indicated in the table. Weigh to the nearest 0.001 mg using a microbalance.
8.2 Fill syringes "5" and "6" with solvent and fill one of the remaining syringes with the sample solution. With the sample chamber at thermal equilibrium, balance the bridge to establish the reference zero as described in 7.6 and 7.7.
8.3 Rinse the sample thermistor with 3 or 4 drops of the sample solution and deposit 1 drop on the thermistor. Start the stop watch. Center the meter with the decade dials and record ΔR at the time interval determined during the standardization for the solvent being employed (7.8). When running a series of samples, check the zero point frequently as described in 7.9.
8.4 Using the appropriate calibration curve, obtain the molarity corresponding to the observed ΔR value.
9. Calculation
9.1 Calculate the relative molecular mass (molecular weight) of the sample as follows:
Relative Molecular Mass (molecular weight) = c/m
where:
c = concentration of sample solution, g/L and
m = molarity of solution, as determined in 8.4.

