ASTM D2427 Standard Test Method for Determination of C2 through C5 Hydrocarbons in Gasolines by Gas Chromatography
9. Calculation
9.1 Calculate the percentage of the individual components using the following procedure that applies and report to the nearest 0.1 %.
9.1.1 Backflush Method - Measure the areas of all of the peaks representing compounds to be reported and that of the internal standard. Adjust each component peak area by use of the proper calibration factor for differences in response between the component and the internal standard. Calibration factors relative to volume or weight percentages can be used. Calculate the percentage of each component as follows:
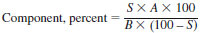
where:
S = percentage of standard,
A = peak area of the component, and
B = peak area of the internal standard.
If a constant volume, rather than internal standard method was used, calculate the percentage of each component by comparing its area to that produced by a known concentration of the component when the same constant volume of a standard sample is charged. A linear concentration - area relationship may be assumed and the percentage of each hydrocarbon calculated using the relation
C1 = C2(A1/A2)
where:
C1 = percentage of component in unknown,
A1 = peak area of component in unknown,
C2 = known percentage of component in standard sample, and
A2 = peak area of component in standard sample.
9.1.2 Reverse Flow Method - Measure the areas of all of the peaks, including the area of the broad peak representing the C6 and heavier portion. Apply the appropriate calibration factors to the areas to correct for the differences in response of the components. Calibration factors relative to volume or weight percentages may be used. Calculate the percentage of each component as follows:
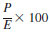
where:
P = corrected peak area, and
E = sum of correlated peak areas.

