1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover the testing of silicone fluids for use in transformers, capacitors, and electronic assemblies as an insulating or cooling medium, or both. These methods are generally suitable for specification acceptance, factory control, referee testing, and research.
1.2 Although some of the test methods listed here apply primarily to petroleum-based fluids, they are, with minor revisions, equally applicable to silicone fluids.
1.3 Silicone fluids are used for electrical insulating purposes because of their stable properties at high and low temperatures and their relative environmental inertness.
1.4 A list of the properties and standards are as follows:
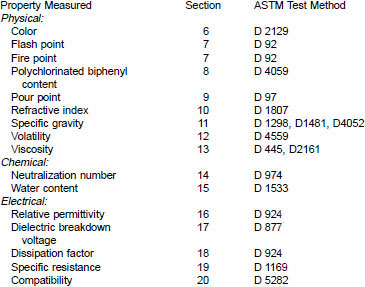
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D92 Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland Open Cup
D97 Test Method for Pour Point of Petroleum Products
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and the Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity)
D877 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using Disk Electrodes
D923 Test Methods for Sampling Electrical Insulating Liquids
D924 Test Method for Dissipation Factor (or Power Factor) and Relative Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Electrical Insulating Liquids
D974 Test Method for Acid and Base Number by Color-Indicator Titration
D1169 Test Method for Specific Resistance (Resistivity) of Electrical Insulating Liquids
D1298 Practice for Density, Relative Density (Specific Gravity), or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by Hydrometer Method
D1481 Test Method for Density and Relative Density (Specific Gravity) of Viscous Materials by Lipkin Bicapillary Pycnometer
D1533 Test Methods for Water in Insulating Liquids (Karl Fischer Reaction Method)
D1807 Test Methods for Refractive Index and Specific Optical Dispersion of Electrical Insulating Liquids
D2129 Test Method for Color of Water White Electrical Insulating Liquids
D2161 Practice for Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Universal Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity
D2864 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulating Liquids and Gases
D4052 Test Method for Density and Relative Density of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D4059 Test Method for Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Insulating Liquids by Gas Chromatography
D4559 Test Method for Volatile Matter in Silicone Fluid
D4652 Specification for Silicone Fluid Used for Electrical Insulation
D5282 Test Methods for Compatibility of Construction Material with Silicone Fluid Used for Electrical Insulation
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 fire point - the temperature at which oil first ignites and burns for at least 5 s when a small test flame is passed across the surface under specified conditions.
3.1.2 flash point - the temperature at which vapors above the oil surface first ignite when a small test flame is passed across the surface under specified conditions.
3.1.3 refractive index - the ratio of the velocity of light (of a specified wavelength) in air at 25°C to its velocity in the substance under test.
3.1.4 specific gravity - the ratio of weight of a given volume of material to the weight of an equal volume of water. In this method, both weights are corrected to weight in vacuum, and the material is at 25°C using hydrometers calibrated at 60/60°F.
3.1.5 volatility - the weight of liquid lost when a specified weight of liquid is held at a specified elevated temperature for a specific period of time.
3.1.6 water content - the amount of water (mg/kg) dissolved in the liquid.
3.1.7 For additional terms refer to Terminology D2864.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Tests covered in this standard may be used for quality control and design considerations.
4.2 Included in each test method is a brief statement describing its significance.
5. Sampling
5.1 Accurate sampling, whether of the complete contents or only parts thereof, is extremely important from the standpoint of elevation of the quality of the product sampled. Obviously, examination of a sample that because of careless sampling procedure or contamination in the sampling equipment is not directly representative, leads to erroneous conclusions concerning quality.
5.2 Sample the silicone fluid in accordance with Test Methods D923.



