ASTM D1796 standard test method for water and sediment in fuel oils by the centrifuge method (Laboratory Procedure)
5. Apparatus
5.1 Centrifuge:
5.1.1 A centrifuge capable of spinning two or more filled cone-shaped 203-mm (8-in.) centrifuge tubes at a speed which can be controlled to give a relative centrifugal force (rcf) of between 500 and 800 at the tip of the tubes shall be used.
5.1.2 The revolving head, trunnion rings, and trunnion cups, including the cushions, shall be soundly constructed to withstand the maximum centrifugal force capable of being delivered by the power source. The trunnion cups and cushions shall firmly support the tubes when the centrifuge is in motion. The centrifuge shall be enclosed by a metal shield or case strong enough to eliminate danger if any breakage occurs.
5.1.3 Calculate the speed of the rotating head in revolutions per minute (rpm) as follows:

where:
rcf = relative centrifugal force, and
d = diameter of swing, mm measured between tips of opposite tubes when in rotating position.
or
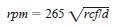
where:
rcf = relative centrifugal force, and
d = diameter of swing (inches) measured between tips of opposite tubes when in rotating position.
5.2 Centrifuge Tubes:
5.2.1 Each centrifuge tube shall be a 203-mm (8-in.) cone-shaped tube, conforming to the dimensions given in Fig. 1 and made of thoroughly annealed glass. The graduations, numbered as shown in Fig. 1, shall be clear and distinct, and the mouth shall be constricted in shape for closure with a cork or solvent-resistant rubber stopper. Scale error tolerances and the smallest graduations between various calibration marks are given in Table 1 and apply to calibrations made with air-free water at 20°C (68°F), when reading the bottom of the shaded meniscus.
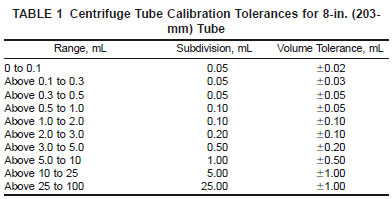
5.2.2 The accuracy of the graduation marks shall be volumetrically verified or gravimetrically certified, in accordance with Practice E 542 using equipment traceable through the National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST). The verification or certification shall include verification for each mark through the 0.5-mL mark; of the 1, 1.5 and 2-mL marks; and of the 50 and 100-mL marks. The tube shall not be used if the scale error exceeds the applicable tolerance in Table 1.
5.3 Bath - The bath shall be either a solid metal block bath or a liquid bath of sufficient depth for immersing the centrifuge tube in the vertical position to the 100-mL mark. Means shall be provided for maintaining the temperature at 49 more or less 1°C (120 more or less 2°F) and 60 more or less 1°C (140 more or less 2°F). See Note 2.
6. Reagents
6.1 Toluene (Warning - Flammable vapor harmful. See Annex A1.) that conforms to Specification D362 or to the IP Specification for Toluol shall be used as the solvent.
6.1.1 The toluene shall be water saturated at 60 more or less 3°C (140 more or less 5°F), but shall be free of suspended water. This may be accomplished by the addition of 2 mL of water per 1000 mL of solvent. Shaking will aid in saturation, but adequate settling time is necessary to ensure that the solvent is free of suspended water before use. See Annex A2 for a procedure for saturating toluene with water.
NOTE 2 - It has been observed for some fuel oils that temperatures higher than 60°C (140°F) may be required to obtain correct sediment and water content. If temperatures higher than 60°C are necessary, they may be used only with the consent of the parties involved. Water saturation of toluene may also be done at this higher testing temperature. (See Appendix X1.)
NOTE 3 - Some oils may require other solvents or solvent-demulsifier combinations. Those agreed upon between the purchaser and the seller may be used.
6.2 Demulsifiers:
6.2.1 Where necessary, a demulsifier should be used to promote the separation of water from the sample, to prevent water from clinging to the walls of the centrifuge tube and to enhance the distinctness of the water-oil interface.
6.2.2 When a demulsifier is used, it should be mixed according to the manufacturer's recommendations and should never be added to the volume of sediment and water determined. The demulsifier should always be used in the form of a demulsifier-solvent stock solution or be premixed with the solvent to be used in the test.
7. Sampling
7.1 Sampling is defined as all steps required to obtain an aliquot of the contents of any pipe, tank, or other system and to place them into the laboratory test container. Only representative samples obtained as specified in Practice D4057 (API MPMS Chapter 8.1) and Practice D4177 (API MPMS Chapter 8.2) shall be used for this test method.
7.2 Practice D5854 (API MPMS Chapter 8.3) contains additional information on sampling and homogenization efficiency of an untested mixer. This test method should not be attempted without strict adherence to Practice D5854 (API MPMS Chapter 8.3).



