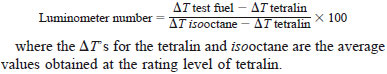9. Procedure
9.1 Introduce 20 mL of tetralin at room temperature into the clean dry sample holder. Place the wick tube into the top of the sample holder and screw tight. Run a small wooden applicator stick into the air vent hole in the bottom of the holder to free the vent of fuel. When the fuel rises to the top of the wick, place the sample holder in the lamp and light it (Warning - Do not allow the flame to come closer than 1/8 in. (3.2 mm) from the thermocouple or the potentiometer (digital indicator-Serial Nos. 378 or higher) to read 1000°F (538°C) or higher). If any soot builds upon the thermocouple shield, put out the flame, clean the shield, lower the sample holder slightly and relight. Through the observation peep hole in the center of the lamp door note that the flame is burning free of smoke (Note 7). Let the tetralin burn at this level for 15 min to warm up the apparatus.
NOTE 7 - All ASTM-CRC Luminometers have been adjusted by the manufacturer to read 45 to 55 at the smoke point of tetralin. If the unit is outside this range, adjust the internal resistor located between the two amplifier tubes (remove the rear cover of the unit) until a meter reading of 45 is obtained.
9.2 After warmup, lower the sample holder until the luminometer meter indicates approximately 30. Rezero the luminometer meter and potentiometer (6.1.3). Turn the luminometer meter switch to the TEST position. Wait at least 30 s for the indicator to stabilize after switching. Operate the luminometer at least 5 min at this position with the outer door closed in a draft-free environment. Record the luminometer meter and temperature indications (Note 8). Raise the wick and its holder until a luminometer reading approximately five units higher is indicated. Allow 5 min and again record the luminometer meter and temperature indications as above. Repeat this procedure until four data points are obtained; the last one being obtained at the flame height where a luminous tail (trace smoke) just breaks out of the tip of the flame. Soot would accumulate on the thermocouple at a slightly higher setting.
9.3 Plot the data points on a luminometer meter reading versus lamp temperature rise curve. All points should fall on a smooth curve. The top point (smoke point of tetralin) will represent rating level (meter reading) for all samples to be tested in this instrument. Repeat four times to establish the average rating level for the instrument (see Fig. 2).
NOTE 8 - The rebalancing can be facilitated by putting a 40 to 60-mesh screen in front of the opening.
9.4 Run two samples of ASTM reference fuel grade iso octane as described in 9.1-9.3, but obtain four data points, two below and two above the rating level established with tetralin for the instrument. (The four data points should be uniformly separated by approximately 10 luminosity units.) One of the samples should be run before running the unknown test fuel; the other sample should be run after running the test fuel. Plot two curves, and at the rating level, find the lamp temperature rise for each sample of iso octane (Fig. 3). Average these values.
9.5 Run one sample of the unknown test fuel in the manner described for iso octane and determine the lamp temperature rise for this fuel (Fig. 4). Use this value and the average DT's of tetralin and isooctane to calculate the luminometer number of this test fuel.
NOTE 9 - If a number of unknown test fuels are to be tested, the second sample of isooctane may be run after all of the unknown test fuels, provided all of these runs are made the same day.
NOTE 10 - Fuels that have high luminometer numbers are prone to form condensation and are greatly affected by air leaks or leveling errors. Preheating the interior of the cabinet with a small drop light, or using a slow step-type warmup will prevent condensation problems. If condensation is encountered, meter readings will become unstable and moisture will appear on the peep-hole glass. If condensation is encountered, it can be removed by allowing the fuel to burn with the lamp door removed until all moisture clears from the filter glass and holder.
NOTE 11 - Fuels that have very low luminometer numbers frequently smoke at relative low meter readings. The absence of a smoking flame with fuels giving a low-temperature rise should be assured by observation through the peep hole in the lamp door. Clean the optical filter and thermocouple shield if a smoky flame has been encountered.
10. Calculation
10.1 Calculate the luminometer number of the test fuel as follows: