ASTM D1533 standard test method water in insulating liquids by Coulometric Karl Fischer Titration
14. Report
14.1 Report the following information:
14.1.1 Water content of the test specimen in mg/kg (ppm) rounded to the nearest integer.
14.1.2 Sample identification.
14.1.3 Sample temperature when collected, if available.
15. Precision and Bias
15.1 Precision:
15.1.1 The following criteria may be used for judging precision of test results on new and used oils at the 95 % probability level. The precision statements for this test method were based on 9 samples and 37 laboratories.
15.1.1.1 Repeatability - The difference between results obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test material, in the long run, would exceed 7 ppm, only 1 case in 20, in the 0 to 50 mg/kg (ppm) range.
15.1.1.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test material, in the long run, would exceed 14 ppm, only 1 case in 20, in the 0 to 50 mg/kg (ppm) range.
15.2 Bias - The bias of the procedure in this test method for measuring water content of electrical insulating fluids has not been determined from the collaborative interlaboratory round-robin study, since there is no suitable standard for which the exact water content is known.
15.3 The typical method detection limit (MDL) at the 95 % confidence level has been found to be 8 ppm water for the mineral oil samples.
NOTE 3 - The MDL is defined here as the minimum concentration of a substance that can be measured and reported with 95 % confidence using a 7 mL oil sample. The value of 8 ppm has been determined from the reproducibility of the results in interlaboratory test of two new and one used oil sample containing about 11 mg/kg (ppm) water.
NOTE 4 - A value of the MDL for an individual laboratory may be calculated from the results of n replications of complete analysis of a sample using the following equation:
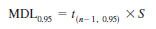
where:
t(n-1, 0.95) = student's t value for n - 1 df and a confidence level of 95 %, and
S = standard deviation of n replicate analyses.
The MDL for an individual laboratory may differ from the MDL of 8 mg/kg (ppm) calculated for this collaborative study.
16. Keywords
16.1 coulometric Karl Fischer titration; free water; Karl Fisher method; Karl Fischer reagent; moisture content; solvent verification solutions; water content

