(Equivalent Test Methods: IP 139, ISO 6618, DIN 51558T1, JIS K 2501, and AFNOR T60-112)
EXPLANATION
See Acid number for Test Method D664 that follows. Oils such as many cutting oils, rustproofing oils, and similar compounded oils, or excessively dark-colored oils, that cannot be analyzed by this test method due to obscurity of the color-indicator end point, can be analyzed by Test Method D664. The acid numbers obtained by this color-indicator test method may or may not be numerically the same as those obtained by Test Method D664.
DEFINITIONS
Acid number - the quantity of base, expressed in milligrams of potassium hydroxide per gram of sample that is required to titrate a sample in this solvent to a green/green-brown end point, using p-naphtholbenzein indicator solution.
Strong acid number - the quantity of base, expressed in milligrams of potassium hydroxide per gram of sample, that is required to titrate a hot water extract of the sample to a golden brown end point, using methyl orange solution.
TEST SUMMARY
To determine the acid number, the sample is dissolved in a mixture of toluene and isopropyl alcohol containing a small amount of water, and the resulting single-phase solution is titrated at room temperature with standard alcoholic base or alcoholic acid solution, respectively, to the end point indicated by the color change of the added p-naphtholbenzein solution (orange in acid and green-brown in base). To determine the strong acid number, a separate portion of the sample is extracted with hot water and the aqueous extract is titrated with potassium hydroxide solution, using methyl orange as an indicator.
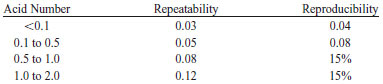
TEST PRECISION